Compare courses from top Australian unis, TAFEs and other training organisations.
Sex in the Workplace
It may be 2014 but there is still a significant gender gap in the job market. Julia takes a look at the industries that are the worst offenders.
Julia Watters
Feb 11,2014
The issue of gender in the workplace is not new. In fact, women’s place in industry was debated long before women got the vote. And while we’re on the topic of women and politics, the Australian parliament is currently experiencing an oestrogen deficit of its own. Sadly, it’s not unusual for most of us to see leadership groups containing only one woman, in this case Julie Bishop. However, as the current cabinet has come after the first Australian female Prime Minister, first female Governor-General and the fleeting but female-packed cabinet of Kevin Rudd’s final spin in the PM chair, people are sitting up and taking notice.
Now don’t get me wrong – I don’t believe anyone should be awarded a position based on anything but his or her suitability for that role. But when I refer to suitability, I’m not referring to their ability to fit into a smoking jacket and enjoy a cigar and a brandy. The reality is that when it comes to gender equality in Australia, women can still relate more to Peggy Olsen from Mad Men than is acceptable in the 21st century.
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), the gender gap still stood firm with 17.6 per cent less women taking part in the workforce than men in November 2012. At the time, women were also earning an average of $261.60 per week less than men. Despite the gap decreasing to 14.9 per cent in November 2004, it remains wider than it was 18 years ago. This is particularly concerning considering that, as recorded in the 2011 Australian Census, over half of the Australian population is female.
The grand canyon
So what industries are the worst offenders? According to ABS the category of financial and insurance services has the largest discrepancy in wages with women earning an average of $610.40 per week less than their male colleagues. Other notable gaps include professional, scientific and technical services ($578.60 weekly gap), mining ($567 weekly gap), and the country’s largest growing industry for employment – health care and social assistance ($562.30 weekly gap).
May 2013 average weekly ordinary time earnings, full-time adults by industry:
Industry |
Males |
Females |
Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial and insurance services | 1944.7 | 1334.3 | 610.4 |
| Professional, scientific and technical services | 1923.3 | 1344.7 | 578.6 |
| Health care and social assistance | 1742.2 | 1179.9 | 562.3 |
| Mining | 2511.4 | 1944 | 567 |
| Rental, hiring and real estate services | 1457.5 | 1115 | 342.5 |
| Construction | 1478.6 | 1145 | 333.6 |
| Information media and telecommunications | 1790.5 | 1471.8 | 318.7 |
| Transport, postal and warehousing | 1476.8 | 1237 | 239.8 |
| Arts and recreation services | 1398.8 | 1168.7 | 230.1 |
| Electricity, gas, water and waste services | 1666.9 | 1447.2 | 219.7 |
| Education and training | 1632.6 | 1417 | 215.6 |
| Manufacturing | 1286.2 | 1086.9 | 169.3 |
| Wholesale trade | 1456.8 | 1308.7 | 148.1 |
| Administrative and support services | 1331 | 1191.3 | 139.7 |
| Other services | 1146.1 | 1033.9 | 112.2 |
| Public administation and safety | 1529 | 1426.8 | 102.2 |
| Accommodation and food services | 1080.8 | 995.5 | 85.3 |
| Retail trade | 1071.8 | 944.6 | 77.2 |
| Average all industries | 1516.4 | 1250.5 | 265.9 |
Follow the (male) leader
Remuneration inconsistencies between the genders aren’t the only gap to be bridged in the workforce. Positions of power, also tied to high salaries, remain severely unlikely to be occupied by women. The 2012 Australian Census of Women, undertaken by the government’s Equal Opportunity for Women in the Workplace Agency (now known as the Workplace Gender Equality Agency), uncovered that women hold a very small share of leadership roles in workforce.
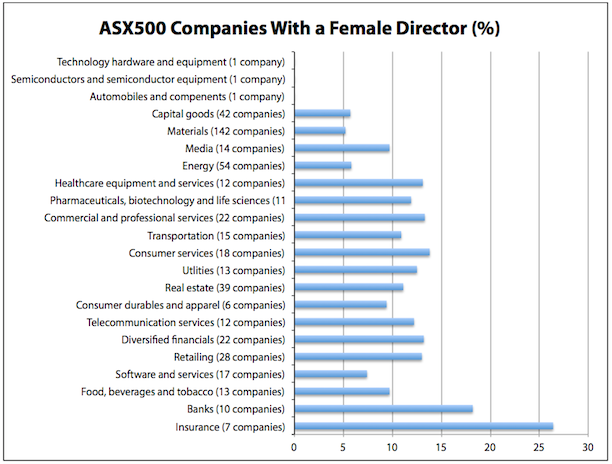
The worst performing industries for women in leadership in ASX500 companies include the automotive industry and the technology, hardware and equipment industry, both with 0 per cent female directors/executives. Top performers included insurance with 26.4 per cent female directors and banks with 18.2 per cent female directors.
Closing the gap
While companies are receiving more pressure to internally audit their human resources gender mix, there is still a long way to go. The government introduced a gender equality reporting framework in 2013 with the purpose of creating industry benchmarks for gender equality and the Workplace Gender Equality Agency continues to publish statistics and recommendations to organisations in an effort to promote more opportunities for women.
Some companies are answering the call of such bodies and the community, but these statistics state clearly that a concerning imbalance remains the norm. The hope is that the new framework and its benchmarks will get equal opportunity back on the agenda and influence greater balance between genders in the Australian workforce.
If you think you're missing out on leadership opportunities because of reasons other than the gender gap, there are plenty of online courses available to help you gain the professional development you're looking for.
About the author
Julia Watters covers topics in career development, educational guidance, and workplace success in her Career FAQs articles.